Introduction
Choosing the right Learning Management System (LMS) is a critical decision for businesses, educational institutions, and training providers. With the increasing demand for online learning, organizations must decide between a SaaS (Software-as-a-Service) LMS and a self-hosted LMS. While upfront costs are an important factor, hidden expenses can significantly impact the long-term budget.
This guide breaks down the cost-benefit analysis of both options, highlighting key considerations like initial investment, maintenance costs, scalability, and LMS integration services. By the end, you’ll have a clear understanding of which LMS aligns best with your organization’s needs and financial goals.
SaaS vs. Self-Hosted LMS: Understanding the Basics
Before diving into cost comparisons, let’s define both options:
SaaS-Based LMS (Cloud-Based)
A SaaS LMS is hosted on the provider’s cloud servers, offering an out-of-the-box solution with automatic updates and vendor-managed maintenance.
Pros:
- Lower upfront costs with a subscription-based model.
- Scales easily—add users and features as needed.
- Automatic security updates and compliance management.
- Quick deployment without requiring extensive IT expertise.
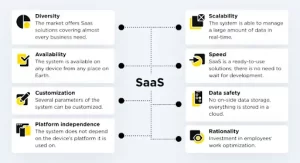
Cons:
- Ongoing subscription fees may increase over time.
- Limited customization—reliant on vendor’s framework.
- Data security concerns—your information is stored on external servers.
Self-Hosted LMS (On-Premise or Private Cloud)
A self-hosted LMS is installed on your own servers, offering complete control over customization and security.
Pros:
- Full control over data privacy and security.
- No recurring SaaS fees, making it cost-effective in the long run.
- Custom LMS development allows for unique training needs.
Cons:
- Higher upfront costs for servers, software, and IT resources.
- Requires an in-house team for maintenance and troubleshooting.
- Scaling up can be complex and expensive.
Cost Breakdown: Upfront vs. Long-Term Expenses
To prevent budget overruns, here’s a side-by-side cost comparison of each LMS model:
| Expense Category | SaaS LMS (Cloud-Based) | Self-Hosted LMS (On-Premise) |
|---|---|---|
| Initial Setup Cost | Low (subscription-based) | High (hardware & setup fees) |
| Customization | Limited options | Full control over development |
| Maintenance & Support | Included in the plan | Requires in-house IT team |
| LMS Integration Services | Vendor-managed | Custom API development needed |
| Scalability | Easy, pay-as-you-grow | Requires additional resources |
Hidden Costs: What Many Buyers Overlook
Beyond the standard pricing, both SaaS and self-hosted LMS platforms come with hidden fees. Being aware of these potential costs can save you from unexpected financial strain.
Hidden Costs of a SaaS LMS:
Additional charges for exceeding user limits.
Premium support plans for faster customer service.
Extra fees for API access and third-party integrations.
Possible price increases due to vendor policy changes.
Hidden Costs of a Self-Hosted LMS:
- Ongoing software updates and security patches.
- Server maintenance, cloud hosting, or data center fees.
- IT staff costs for troubleshooting and system upkeep.
- Compliance costs for GDPR, HIPAA, or other regulations.
Real-World Example: A Mid-Sized Corporate Training Firm
A mid-sized corporate training company faced a tough decision between SaaS and self-hosted LMS solutions. Initially, SaaS seemed like the better option due to lower startup costs. However, after analyzing long-term expenses, they discovered:
Their rapid growth meant their user base would exceed SaaS pricing tiers within a year.
They needed deep LMS integration services with their existing HR and CRM systems.
Industry data privacy regulations required full control over user information.
To future-proof their investment, they chose a self-hosted LMS, invested in scalable cloud hosting, and hired an IT specialist for maintenance. Within three years, they broke even on initial costs and built a fully customized, secure learning platform.
Key Considerations for LMS Buyers
Before making a decision, assess the following:
- Budget Constraints: SaaS offers a lower-cost entry, while self-hosted LMS solutions are cost-effective over time.
- Customization Needs: If you require unique features, a self-hosted LMS offers more flexibility.
- LMS Integration Services: If you need deep integrations with tools like Salesforce, HR systems, or custom analytics, ensure the LMS can support it.
- Long-Term Vision: Avoid short-term savings that could result in higher expenses as you scale.
Conclusion
Both SaaS and self-hosted LMS solutions have advantages and trade-offs. SaaS LMS is ideal for organizations seeking quick deployment, minimal IT maintenance, and built-in support, while self-hosted LMS solutions provide greater control, customization, and long-term cost savings.
By conducting a thorough cost-benefit analysis—including hidden fees—you can make a strategic decision that maximizes your LMS investment.
Call to Action
Still unsure which LMS is right for your organization? Our experts can help! We specialize in:
LMS integration services
Affordable LMS setup
Custom eLearning solutions
Contact us today to find the best LMS solution for your needs!